
How to Use CHKDSK Commands on Windows 10?
CHKDSK (check disk) is one of the most efficient ways to ensure that all the hard disks on your system are working well. Windows OS from Windows XP to Windows 10, all of them have the chkdsk feature.
Using the utility, you can repair most of the disk errors on your OS. it can also be used to speed up your Windows OS too. There is no need to download any file, or to perform a new installation on your OS. Use the chkdsk command to repair any error on your Windows 10.
Table of Contents
Use chkdsk commands on Windows 10

There are three different ways to use chkdsk commands on your Windows OS.
- There is option to use CMD (Command Prompt).
- You can also the Scan Drive Utility
- With Windows 10 bootable drive, you can also use the chkdsk command.
Chkdsk on CMD
To use chkdsk with CMD here is how to do it:
- Go to Start menu in the bottom left of your screen.
- Type “CMD” in Start menu and right click on Command Prompt. Run the application as administrator.
- Inside the CMD type “Chkdsk C: /f /r /x”.
- You will be asked to type Y for continuing. Type “y” and press Enter.
- Checking will take place. once completed, restart your system.
Note: Here the /f is used to fix errors in your disk. /r is used to locate bad sectors, /x for recovering readable info from your disk, and C: here is the letter of the disk.
Using the Utility from My Computer
For Windows 10 users, they will find My PC instead of My Computer on their desktop.
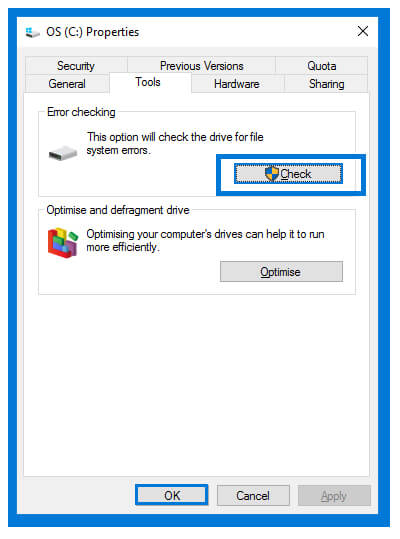
- Open My Computer and right click on the disk that you want to run the utility.
- Now, click on Properties, and click on Check in Tools section.
- Clicking on Check will open another window. Select the Scan drive option.
- “You don’t need to scan this drive. We haven’t found any errors on this drive. You can still scan the drive for errors if you want.” will be found below Scan Drive.
Soon your system will scan any errors (if found) and will try to fix them. Normally you will experience two states:
For no errors in your disk
Your drive was successfully scanned Windows successfully scanned the drive. No errors were found. Your drive was successfully scanned Windows successfully scanned the drive. No errors were found.
For errors in your disk
Restart your computer to repair the file system. You can restart right away or schedule the error fixing on the next restart.
Run chkdsk from Windows 10 installation
For this method, you will need to possess a bootable USB drive of Windows 10. You will need to download Windows 10 and make it bootable using third-party applications like Rufus. Once created, you will use it to run chkdsk.
- Insert the bootable USB and restart your system.
- Now, system will boot the USB and you will see “Press any key to boot from CD or DVD”. You will need to press any keys form your keyboard to enter the setup.
- Soon will be placed to select Language, Time and Keyboard method.
- Then you will be place to installation of Windows. Click on Next.
- In the step you will need to click on Repair your computer.
- In Choose an option section, you will need to select Troubleshoot.

The system will troubleshoot any problem that is present on your hard drives and will fix them too. Once the checking and repairing got completed, then you can restart the system to be used again.
Command and parameters
For making things easier, here are some commands and their parameters.
<volume> Specifies the drive letter (followed by a colon), mount point, or volume name.
[ [<path>] <filename> Use with file allocation table (FAT) and FAT32 only. Specifies the location and name of a file or set of files that you want chkdsk to check for fragmentation. You can use the ? and * wildcard characters to specify multiple files.
/c is used for only NTFS volumes only.
/f is used to fix errors on any disk that you selected.
/l is used only in NTFS volumes. It is used to perform the checking of index entries.
/i is used only in NTFS volumes. It is used to perform the checking of index entries. It is used for less vigorous checking.
/r implies that /f and /p. Is used to locate bad sectors.
/v is used to display the name of each file, and also to show every directory.
/x forces volume to dismount.
/b for only NTFS volumes. It is used to rescan and also to free clusters of errors.
/scan in NTFS volumes. Is used to scan your drive online.
/scan, NTFS, online scan
/forceofflinefix Use with NTFS only (must be used with /scan). Bypass all online repair; all defects found are queued for offline repair (for example, chkdsk /spotfix).
/perf Use with NTFS only (must be used with /scan). Uses more system resources to complete a scan as fast as possible. This may have a negative performance impact on other tasks running on the system.
/spotfix Use with NTFS only. Runs spot fixing on the volume.
/sdcleanup Use with NTFS only. Garbage collects unneeded security descriptor data (implies /f).
/offlinescanandfix Runs an offline scan and fixes the volume.
/freeorphanedchains Use with FAT/FAT32/exFAT only. Frees any orphaned cluster chains instead of recovering their contents.
/markclean Use with FAT/FAT32/exFAT only. Marks the volume clean if no corruption was detected, even if /f was not specified.
/? Displays help at the command prompt.
Depending on the utility, CMD, or Recovery Console the command parameters can be changed.
/p can be used to fix errors and it can also be used for read-only.
Trouble shooting
Different errors can be found while using the commands. If you got “Errors found. CHKDSK cannot continue in read-only mode.” then you have run with /r. you can use the following to fix it:
chkdsk /f
“Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked?” for such errors, you will need to type Y and press Enter.
If you got “Cannot lock current drive.” then you can use:
Chkdsk /r

